ln x taylor series expansion|taylor series of ln 1+x : Cebu You got the general expansion about $x=a$. Here we are intended to take . Yes. Download Asana for iPhone and iPad in the App Store. Download Asana for Android phones in the Google Play Store. We recommend visiting the Stores from your phone for the smoothest experience. Download Asana for desktop here for your Mac, Windows (64-bit), or Windows (32-bit).
0 · taylor series of ln 1+x
1 · taylor series for ln x+1
2 · taylor series expansion calculator
3 · taylor expansion of log x
4 · taylor expansion of ln x+1
5 · taylor expansion for ln 1+x
6 · series expansion of log x
7 · series expansion of ln 1+x
No MasterDica, você confere as melhores dicas de filmes e séries nos principais serviços de streamings disponíveis no Brasil. . Naquele fim de semana é um filme de suspense que vai te conquistar logo no início! Filmes. FILMAÇO DE FAROESTE CLÁSSICO é um tesouro escondido e PODE SER VISTO DE GRAÇA
ln x taylor series expansion*******$$f(x)=\ln(x).$$ The Taylor expansion around $a$ is $$f(x)=\sum_{n=0}^{\infty} \frac{f^{(n)}(a)}{n!}(x-a)^n,$$ so for $a = 1$, $$f'(x) = \frac{1}{x},\; f''(x) = \frac{-1}{x^2},\; f^{(3)}(x) = \frac{2}{x^3},\ldots,\; f^{(n)}(x) = \frac{(-1)^{n-1}(n .
You got the general expansion about $x=a$. Here we are intended to take .If you know the Taylor expansion for $\ln(1+t)$, that is, $$ .taylor series of ln 1+x So you would like to solve for #f(x) = ln(x)# at #x=1# which I assume mean centered at #1# of which you would make #a=1# To solve: #f(x) = ln(x)# and #f(1) = ln(1) .Pictured is an accurate approximation of sin x around the point x = 0. The pink curve is a polynomial of degree seven: The error in this approximation is no more than |x| / 9!. For a full cycle centered at the origin (−π < x < π) the error is less than 0.08215. In particular, for −1 < x < 1, the error is less than 0.000003. The Taylor expansion for \(\ln x\) given in Key Idea 32 is centered at \(x=1\),so we will center the series for \(\ln (\sqrt{x})\) at \(x=1\) as well. With \[\ln x = .
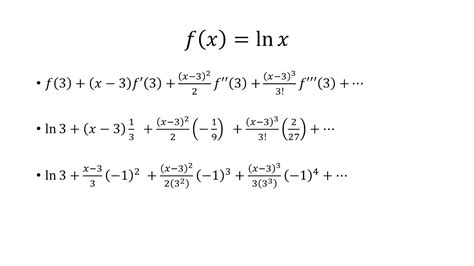
You got the general expansion about $x=a$. Here we are intended to take $a=0$. That is, we are finding the Maclaurin series of $\ln(1+x)$. That will simplify your expression .Representing Functions with Taylor and Maclaurin Series. We now discuss issues of convergence for Taylor series. We begin by showing how to find a Taylor series for a .
A calculator for finding the expansion and form of the Taylor Series of a given function. To find the Maclaurin Series simply set your Point to zero (0).
taylor series of ln (x) Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals.
Recognize the Taylor series expansions of common functions. Recognize and apply techniques to find the Taylor series for a function. Use Taylor series to solve . If you know the Taylor expansion for $\ln(1+t)$, that is, $$ \ln(1+t)=\sum_{n\ge1}\frac{(-1)^{n+1}t^n}{n}\tag{*} $$ which follows from integrating $$ .Taylor Series. 1. Taylor Series. Our aim is to find a polynomial that gives us a good approximation to some function. (See why we want to do this in the Introduction .) We find the desired polynomial approximation using the Taylor Series. If we want a good approximation to the function in the region near \displaystyle {x}= {a} x = a, we need to .
Wolfram|Alpha brings expert-level knowledge and capabilities to the broadest possible range of people—spanning all professions and education levels.
1. That limit doesn't exist - |ln(x)| | l n ( x) | tends to infinty, as does 1/x 1 / x, so the limit is not defined. – Fahrenheit997. Jan 24, 2017 at 17:04. The limit does exist -- it is +∞ + ∞. (The limit has to be as x → 0+ x → 0 +, since ln ln is not defined for negative numbers.) – Clement C. Jan 24, 2017 at 18:30.
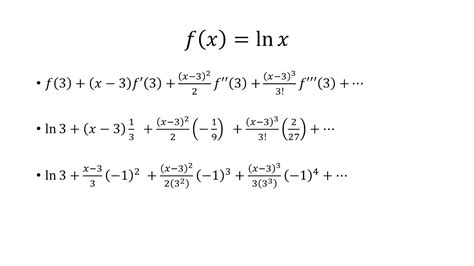
Note that the Taylor expansion for ln(1+x) can be easily derived by integrating eq. (2). ln(1+x) = Z x 0 1 1+t . The series given in eq. (6) diverges at x = −1 and is conditionally convergent at x = 1. Likewise, we can obtain the Taylor series for ln(1−x) by either X .常用泰勒级数展开式是高等数学中的重要知识点,本文收集了指数函数、双曲函数、三角函数、反三角函数和对数函数的泰勒级数展开式,并给出了相应的推导过程和示例。如果你想复习或学习这些公式,不妨点击阅读。
Contact us | Advertising & Sponsorship | Partnership | Link to us © 2000-2023 Math.com. All rights reserved. Legal Notices.Please read our Privacy Policy.Privacy
taylor series of ln (x) Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals. For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music..
다시 정리해서, 테일러 급수를 정의하면 아래와 같습니다. A Taylor series is a mathematical representation of a function as an infinite sum of terms, where each term is derived from the function's derivatives at a specific point, typically used for approximating the function's behavior near that point. 간단히 말해 .
This is part of series of videos developed by Mathematics faculty at the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics. This video explains the Taylor Ser.The natural logarithm of a number is its logarithm to the base of the mathematical constant e, which is an irrational and transcendental number approximately equal to 2.718281828459.[1] The natural logarithm of x is generally written as ln x, loge x, or sometimes, if the base e is implicit, simply log x.[2][3] Parentheses are sometimes added .ln x taylor series expansionFree Taylor Series calculator - Find the Taylor series representation of functions step-by-step2 Taylor series: functions of two variables If a function f: IR2!IR is su ciently smooth near some point ( x;y ) then it has an m-th order Taylor series expansion which converges to the function as m!1. Expressions for m-th order expansions are complicated to write down. Taylor Series of ln(x) at x = 2, problem from James Stewart calculus. Need to prepare for your calc 2 final? Check out my "100 Calculus 2 problems ultimate r.Tf(x) = ∞ ∑ k = 0f ( k) (a) k! (x − a)k. In the special case where a = 0 in Equation 8.5.50, the Taylor series is also called the Maclaurin series for f. From Example 8.5.1 we know the nth order Taylor polynomial centered at 0 for the exponential function ex; thus, the Maclaurin series for ex is. ∞ ∑ k = 0xk k!.
So the function which is 1 at x = 0 and sinx x elsewhere has power series expansion 1 − x2 3! + x4 5! − x6 7! + ⋯. Now substitute (2) for 1 + t in (1). Thus t = − x2 3! + x4 5! − x6 7! + ⋯. Make sure not to compute too far. So throw away all terms in powers of x greater than 6. Because the expression (2) has no x term, you will only .Stack Exchange Network Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers. Hints: $$\log x=(x-1)-\frac{(x-1)^2}{2 The value of ln (x) for any x in the range of 0 < x <= 2 can be estimated using the Taylor series as shown below. As more terms are added the results should get better. lnx= (x-1)- (x-1)^2/2+ (x-1)^3/3- (x-1)^4/4.. Write a script file that takes as user inputs the value of x (between 0 and 2) and the number of terms to use N. The program .
The series expansion of ln(x) is derived using the Taylor series, which is a mathematical tool that allows us to express a function as an infinite sum of its derivatives at a given point. In the case of ln(x), the Taylor series is centered at x=1, and the derivatives are evaluated at x=1.
webCifra: Principal (violão e guitarra) Favoritar Cifra. Tom: G. G . A minha alma quer contemplar-te. D G . Ó meu fiel e amado Jesus. G G . Quero servi-Te, quero seguir-Te. .
ln x taylor series expansion|taylor series of ln 1+x